BASIC BUILDING PARAMETERS
The basic parameters that define a pre-engineered building are:
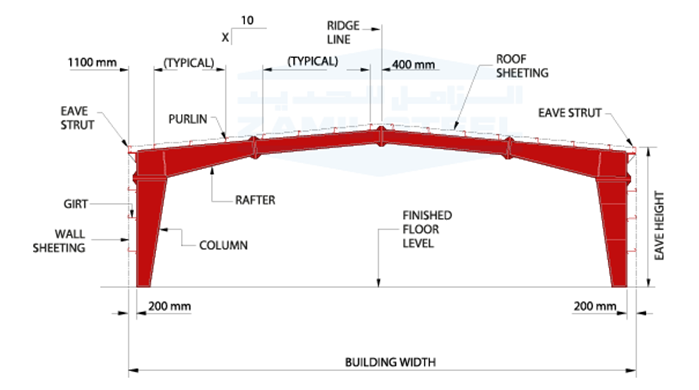
BUILDING LENGTH The longitudinal length of the building measured from out to out of end wall steel lines
Building Height can be defined in three different ways.
1. Clear Height is defined as the height of building from the FFL to the bottom flange of main frame rafter. It is minimum possible clear height throughout the building.
2. Eave Height of the building is the distance between the finish floor level to the top of outer point of eave purlin or eave strut.
3. Peak / Ridge Height is the distance between the FFL and highest/peak point of the building (ridge line.)
BUILDING WIDTH is distance from outside of sidewall girt flange to the outside of opposite sidewall girt flange. This does not include width of lean to area, canopy or roof extension. These limits are also termed as steel line.
ROOF SLOPE is the angle of roof with respect to horizontal. Any particular roof slope is possible, however generally roof slope 0.5: 10 to 1.5: 10 is used considering the economy and aesthetics. For bulk storage roof slope is also dependent upon the angle of repose of that particular material.
END BAY LENGTH The distance from outside of the outer flange of endwall columns to center line of the first interior frame column.
INTERIOR BAY LENGTH: The distance between the center lines of two adjacent interior main frame columns. The most common bay lengths are 6 m, 7.5 m and 9 m.
DESIGN LOADS: Unless otherwise specified Steel pre-engineered buildings are designed for the following minimum loads:
Roof Live Load: 0.57 kN/m2
Design Wind Speed: 110 km/h
Design for snow loads, earth quake loads, collateral loads, crane loads or any other loading condition, if required must be specified at the time of request for quotation.
Loads are applied in accordance with the latest American codes and standards applicable to pre-engineered buildings unless otherwise requested at the time of request for quotation.